GOALS
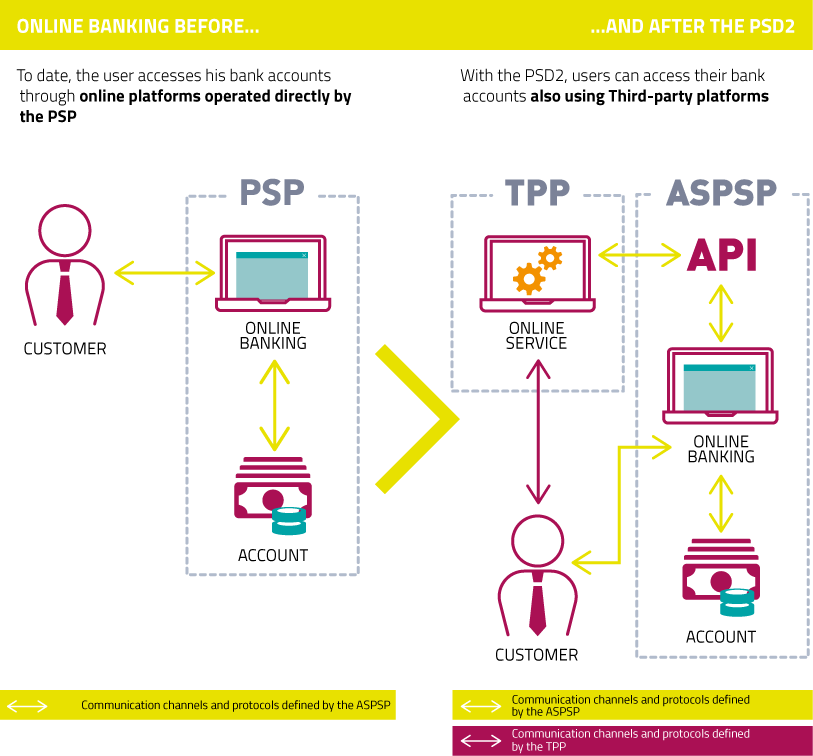
The evolution of the market of payment services is accelerating at high speed, driven by continuous technological innovation and by the significant current legislative changes, that are reshaping the rules of the market.
In order to increase pan-European competition by extending its validity even to non-bank parties and, at the same time, to harmonise the rules to ensure the safety of consumers, in 2007 the first Payments Service Directive (PSD) was adopted.
It had in fact provided for the introduction of a regulatory framework for the SEPA (Single Euro Payments Area) concerning payments within the European area.
Over the past decade, since the entry into force of the PSD, the evolution in digital technologies and the entry of new operators from the Fintech world in the financial sector have identified the urgency for a review and definition of the PSD in the light of the new scenarios considered as “out of scope” in the initial legislation.
The aim of the Directive 2015/2366/EU, known as
PSD2 , is in fact expanding the scope of the PSD:
- improving payment security and consumer protection
- encouraging innovation and competition
- ensuring the same level playing field to all players on the market, including new ones and those who will come forth in the future in the payments market
LEADING PLAYERS
FRAMEWORK
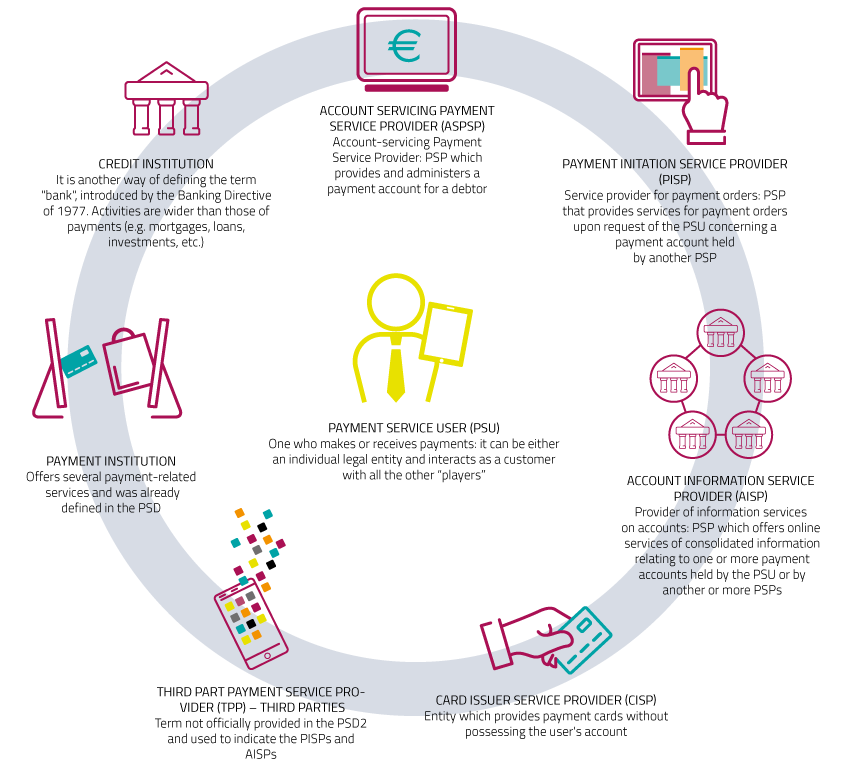
In particular, the PSD2 governs other activities of PSPs in the European market of payment services by introducing three service models, under which new players can build the services they offer.
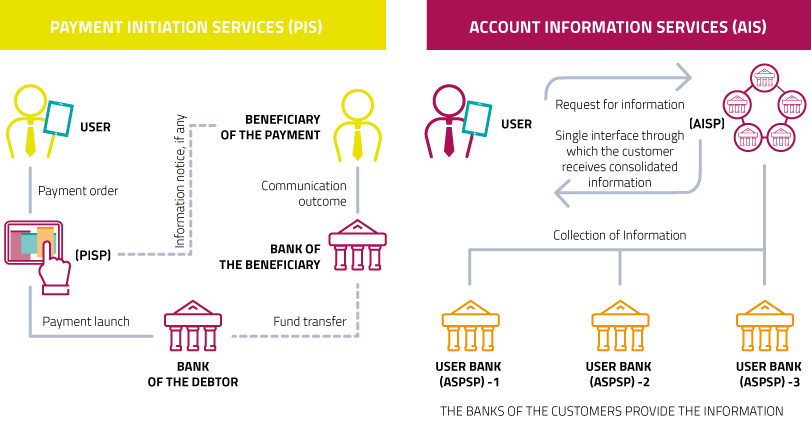
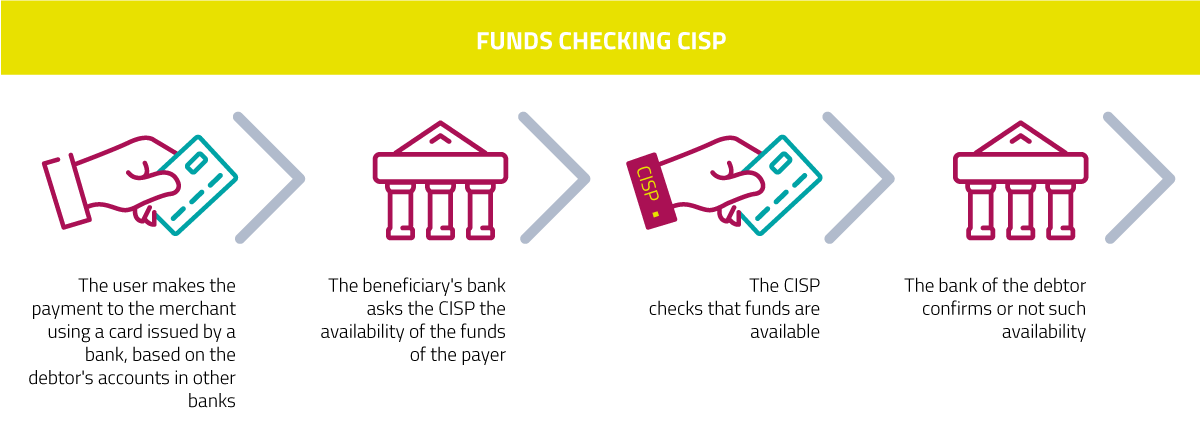
The PSD2 is a potential forge for creating innovative transactional products and services that will be increasingly in line with the digitisation and evolution of customers. In this sense, the market evolution will be considerable, and to date not entirely conceivable, also thanks to the expansion of the Fintech scenario.
With the introduction of the PSD2, the payment industry is evolving in terms of security and reliability for the Retail and Corporate banking markets, granting high levels of competitiveness thanks to the availability of secure, proprietary channels between Banks and non-banking institutes, also known as Payment Service Providers (PSPs).
Security, in accessing your own banking account or in executing electronic payments, is the main objective of the directive: the PSD2 introduces the concept of Strong Customer Authentication (SCA), as the main way for the Payment Service User to access their own data based on something only they know, or possess.
For more info about the new security procedures introduced by the PSD2, head to the Carte di pagamento online e sicurezza - L’autenticazione forte del cliente (SCA) page, published by the Bank of Italy, dedicated to online payments executed through the use of payment cards.
